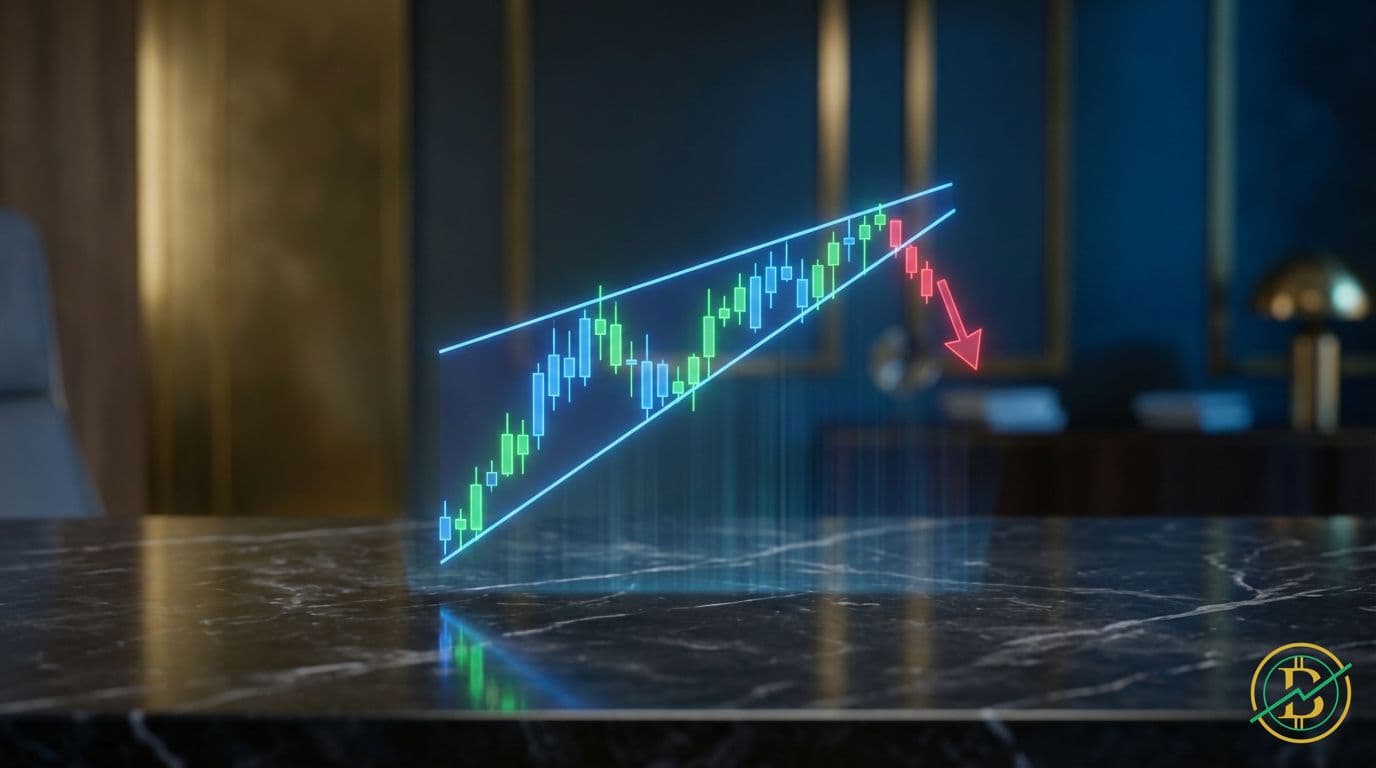
Rising Wedge Pattern in Cryptocurrency Trading
A rising wedge is a bearish chart pattern suggesting a potential price reversal. It forms when price consolidates within an upward-sloping channel, often signaling a coming decline.
Definition
Imagine a price chart for a cryptocurrency. Sometimes, you'll see the price moving upwards, but the rate of increase gradually slows down. The price is like a balloon, and the slowing increase is like the air slowly escaping. A rising wedge is a chart pattern that forms when the price of an asset is making higher highs and higher lows, but the highs are not increasing as much as the lows. This creates a narrowing, upward-sloping channel. It's a technical indicator that traders use to anticipate potential changes in price direction.
Key Takeaway
The rising wedge is generally considered a bearish pattern, suggesting that the price is likely to break downwards.
Mechanics
The rising wedge pattern has a distinctive look. It's formed by drawing two converging trendlines, both sloping upwards. These lines connect a series of higher highs and higher lows. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- Uptrend, but Slowing: The price of the cryptocurrency must be generally increasing, but the rate of increase starts to decelerate. Think of it like a car accelerating, then slowing down gradually.
- Higher Highs and Higher Lows: The price makes a series of higher highs and higher lows. Each peak is higher than the last, and each trough is also higher than the previous one. However, the distance between the highs is shrinking.
- Converging Trendlines: You can draw two trendlines to connect these highs and lows. The upper trendline connects the highs, and the lower trendline connects the lows. These lines should converge, forming a wedge shape. The slope of both lines is upward.
- Volume: Ideally, the volume should decrease as the price moves within the wedge. This indicates weakening buying pressure.
- Breakdown: The pattern is confirmed when the price breaks below the lower trendline. This is the signal that the price is likely to continue its downward move.
Trading Relevance
Traders use the rising wedge pattern to identify potential short-selling opportunities or to take profits on long positions. Here's how it works:
A short position is a trade that profits from a price decrease.
- Identification: Spot the rising wedge pattern on a price chart.
- Confirmation: Wait for the price to break below the lower trendline. This is the confirmation signal.
- Entry: Enter a short position (or close a long position) when the price breaks below the lower trendline. Some traders wait for a retest of the trendline (price briefly goes back up to test it) before entering the trade.
- Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order above the upper trendline or the recent high. This will limit your losses if the price moves against you.
- Take Profit: Determine a profit target. A common method is to measure the height of the wedge and project that distance downwards from the breakdown point. However, it's a good idea to take partial profits along the way.
Why does price move? The price moves due to supply and demand. In a rising wedge, the demand (buying pressure) is weakening, while the supply (selling pressure) is increasing. Eventually, the supply overwhelms the demand, and the price breaks down.
Risks
Trading the rising wedge pattern carries risks:
- False Breakouts: Sometimes, the price can break below the lower trendline (a false breakout) and then quickly reverse and move higher. This is why it's crucial to wait for confirmation (e.g., a candle closing below the trendline) before entering a trade.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are volatile. The price can move rapidly, making it difficult to execute trades and manage risk.
- Market Conditions: The pattern may not always play out as expected, especially during periods of high market volatility or strong overall trends.
History/Examples
While specific historical examples are difficult to pinpoint precisely without detailed data, the rising wedge pattern can be observed across various cryptocurrencies and timeframes. The key is to look for the characteristic converging trendlines and the price action within them. A good example would be analyzing the Bitcoin chart during periods of consolidation before significant price drops. The pattern has been observed in the lead-up to significant price corrections in various altcoins as well.
⚡Trading Benefits
20% CashbackLifetime cashback on all your trades.
- 20% fees back — on every trade
- Paid out directly by the exchange
- Set up in 2 minutes
Affiliate links · No extra cost to you
20%
Cashback
Example savings
$1,000 in fees
→ $200 back